Hi/Low Alarm Kit Instructions
robinmitchell2023-12-27T15:59:58+00:00Hi/Low Alarm Kit Instructions
Table of Contents

Introduction
What is the Hi/Low Alarm?
The Hi/Low Alarm Kit is an alarm circuit that sounds a beeper when a measured voltage becomes too small or too large. The detection point for both the low and high voltage levels can be set using the two onboard potentiometers, and the rate of beeping can also be changed with another potentiometer.
This kit uses an LM358 as a dual comparator to detect both low and high conditions, and a 4093 quad NAND Schmitt trigger provides tone generation and gating.
How can the Hi/Low Alarm be used?
This kit has two primary uses, with the first being the detection of dangerous operating conditions, and the second being the detection of sensor readings out of range.
In the case of dangerous operating conditions, this kit can be used to monitor the output voltage of a power supply, and sound an alarm if that voltage becomes too small or too large (such as in battery charging applications).
In the case of sensor readings, this kit can be used to control devices that react to changes in sensor outputs. For example, a water level monitor could use this to sound an alarm if a water tank needs filling or automatically power a pump to refill the tank with water.

Schematic

Simulation
How Does The Hi/Low Alarm WOrk?
The Hi/Low Alarm consists of three main circuit sub-blocks; a comparator stage, an RTL NOR gate, and a gated tone generator.
To start, an external voltage is fed into VIN (J2), which passes through a potential divider consisting of R1 and R2. The extremely low value of R1 compared to R2 (100Ω << 100KΩ) means that the voltage across R2 is almost identical to the voltage being fed into VIN. The purpose of R1 is to provide some series limiting the current that could otherwise damage the circuit should a fault occur on the VIN input.
This voltage across R2 (which is the same as the voltage on VIN), is fed into two different comparators, U1A, and U1B, which each have their own separate potentiometer.
U1A is configured as a non-inverting comparator which will output a logical 1 when the voltage present on VIN is larger than the voltage set by the potentiometer RV1. This op-amp indicates a “voltage high” condition, and is also connected to the LED D2.
U1B is configured as an inverting comparator that will output a logical 1 when the voltage present at VIN is smaller than the voltage set by the potentiometer RV2. This op-amp indicates a “voltage low” condition, and is also connected to the LED D1.
Each comparator has an additional pull-down transistor on their outputs, and the combination of R5, Q1, and Q2 makes an RTL NOR gate. Simply put, if any of the comparators outputs a logical 1, the voltage at the input of U2A will be pulled down to ground (i.e., 0V).
If the input to U2A is pulled to ground, the output of U2A will switch to 1 as it is configured as an inverter. The second NAND gate, U2B, is configured as a tone generator with R6, RV3, and C1 (see inverting Schmitt trigger oscillator). If the output of U2A is a logical 1, the tone generator U2B outputs a square wave whose frequency is dependent on the resistance of RV3.
Finally, the output of the tone generator is connected to another NAND gate configured as an inverter (U2C), and this, in turn, powers a buzzer controlled by Q3. The diode D1 prevents the buzzer from generating large negative voltages that can damage the transistor Q3.
Component List
| Component | PCB Reference | Quantity | Looks Like |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 DIP Socket | U1 | 1 | |
| 14 DIP Socket | U2 | 1 | |
| LM358 IC | U1 | 1 | |
| 4093 IC | U2 | 1 |  |
| 100R Resistor | R1, R6 | 2 |  |
| 1K Resistor | R5, R7, R8, R9 | 4 | 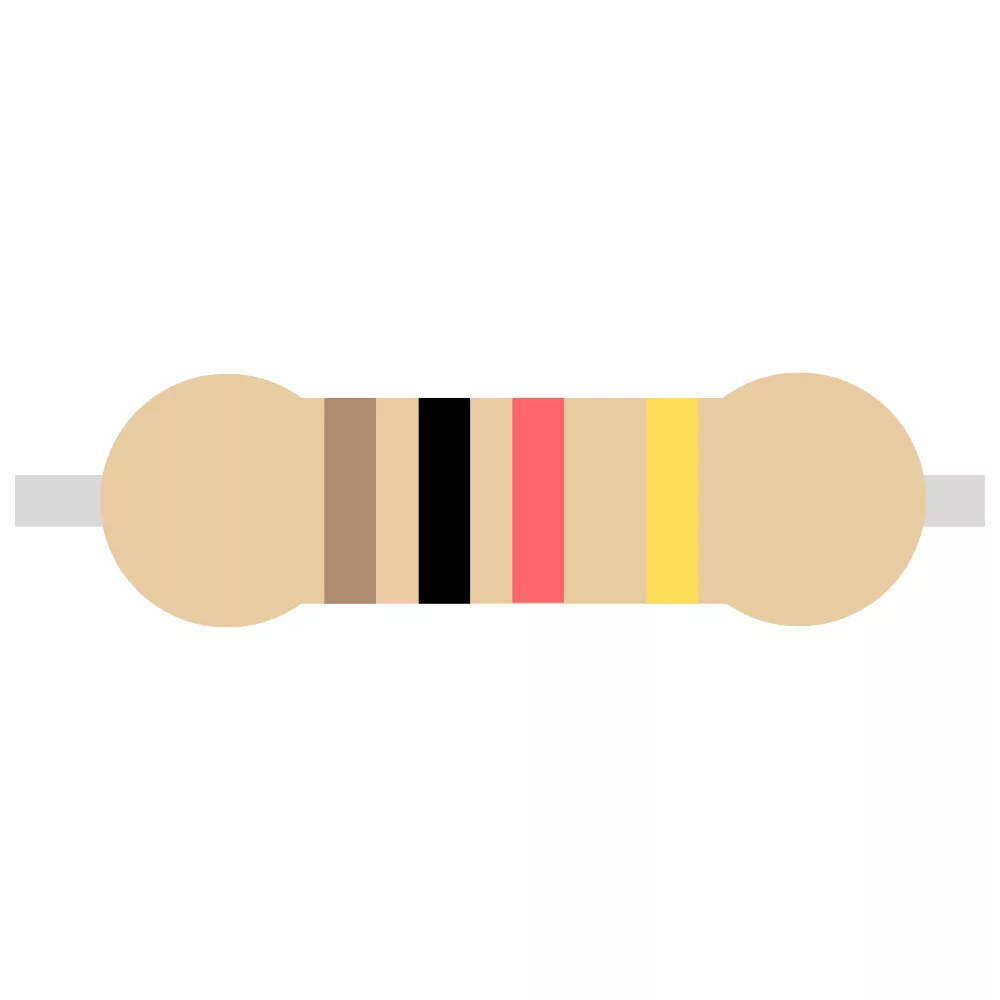 |
| 10K Resistor | R3, R4 | 2 |  |
| 100K Resistor | R2 | 1 |  |
| 10K Potentiometer | RV1, RV2, RV3 | 3 |  |
| 100nF Capacitor | C2, C3 | 2 |  |
| 100uF Capacitor | C1 | 1 | |
| 3mm Red LED | D2, D3 | 2 | |
| 1N5817 Diode | D1 | 1 |  |
| 2N3904 BJT NPN Transistor | Q1, Q2, Q3 | 3 |  |
| Buzzer | BZ1 | 1 | 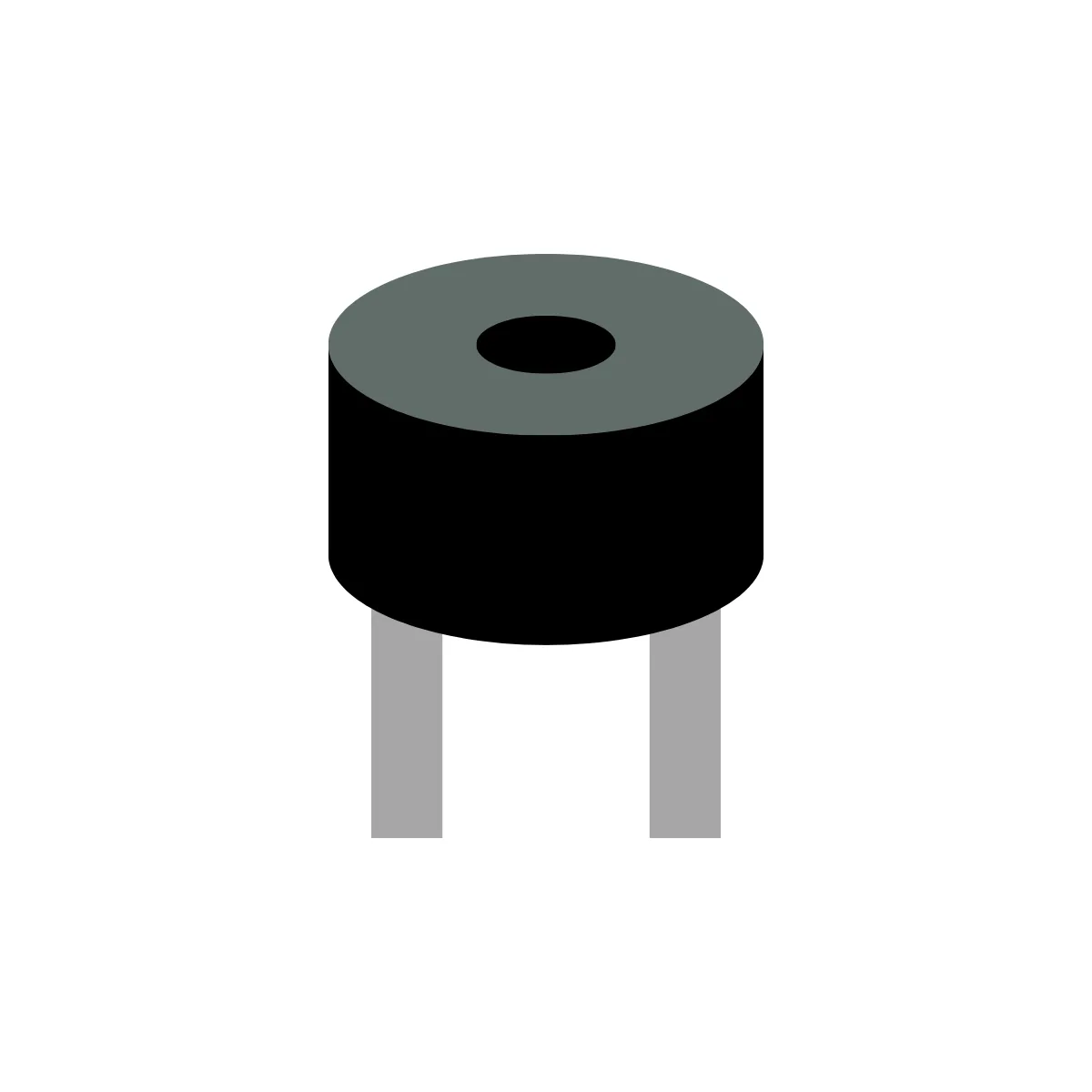 |
| Red Wire | J1 | 1 | 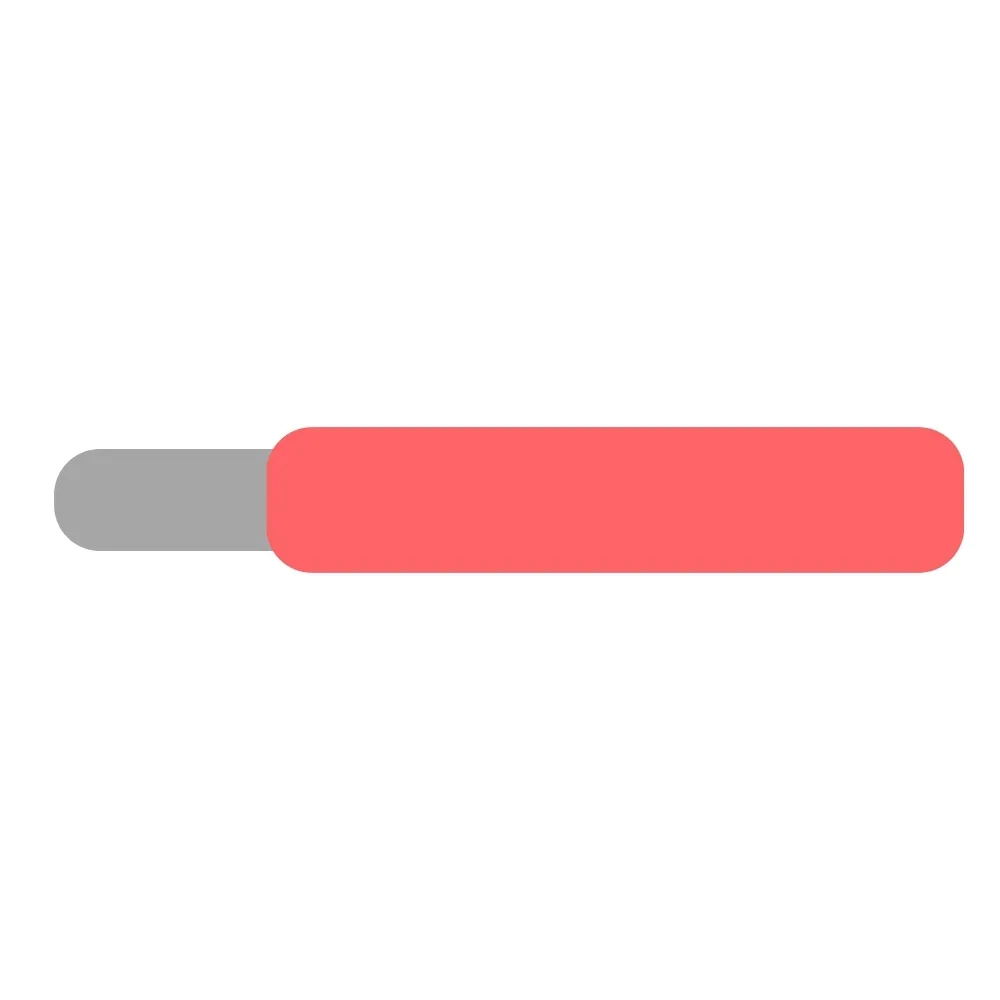 |
| Green Wire | J2 | 1 | 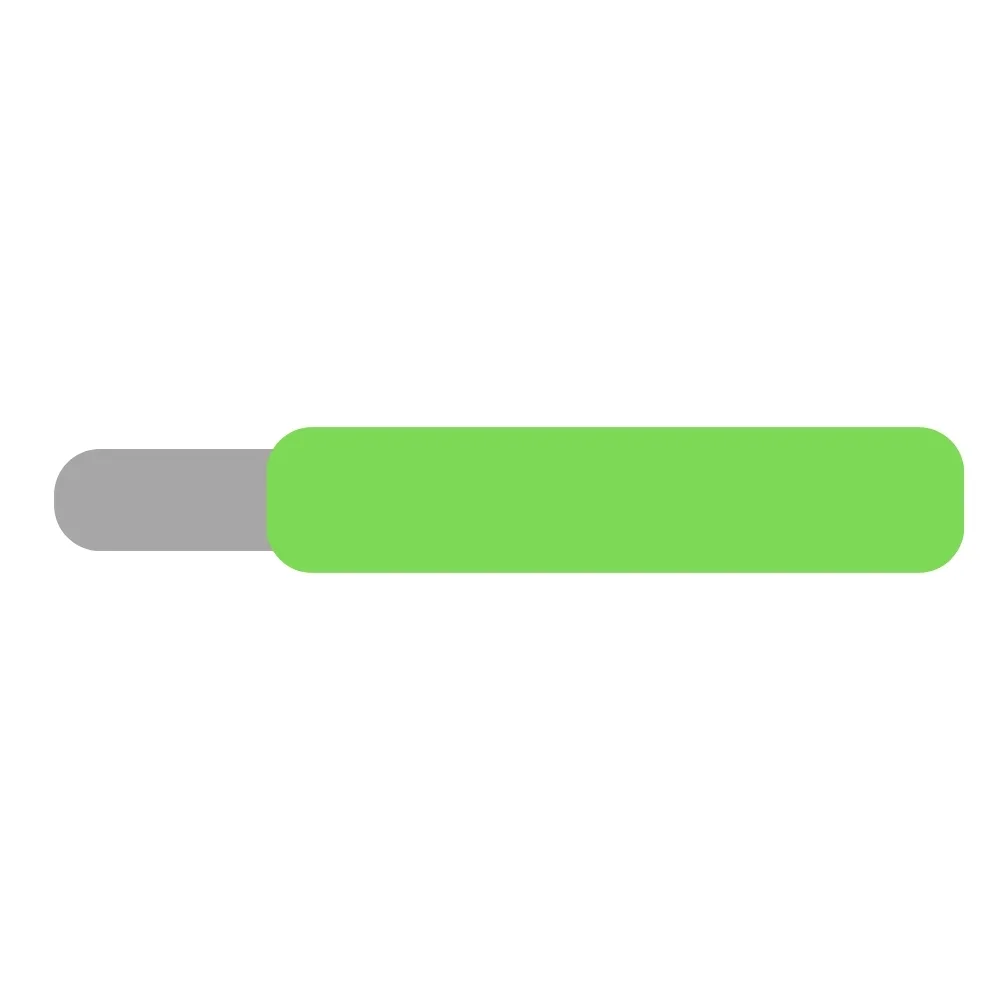 |
| Black Wire | J1, J2 | 2 |  |
PCB


Project Ideas
Power Supply Monitor
The Hi/Low Alarm kit can be used to monitor the voltage output of a power supply and warn nearby users if the power supply voltage drifts too much. This can be extremely important in applications where circuits cannot tolerate large changes in supply voltage (such as microcontrollers and microprocessors), as well as circuits that are under test (such as in laboratory conditions).

Water Tank Controller
The Hi/Low Alarm kit can be used to monitor the voltage output of a power supply and warn nearby users if the power supply voltage drifts too much. This can be extremely important in applications where circuits cannot tolerate large changes in supply voltage (such as microcontrollers and microprocessors), as well as circuits that are under test (such as in laboratory conditions).

Construction Tips

Electronics Construction Guide
To learn more about how to solder electronic components, download the Electronics Construction Manual free using the button below
Component Order
Solder the components in this order to keep things simple
- Resistors
- IC Sockets
- Capacitors
- LEDs
- Potentiometers
- Transistors
- Buzzer
- Wires
Double-check your components BEFORE soldering!
- MitchElectronics kits use double-sided PCBs with plated through-holes
- This makes the PCBs extremely strong
- It also makes desoldering very hard, so be sure components are inserted correctly

Final Thoughts
Connect the outputs to other circuits!
- The separate Hi and Low outputs allow for connecting other circuits
- Consider using a relay driver to automatically control devices
