Latest // 5V Tolerant RP-Duino
Take Your Projects to the Next Level with the RP-Duino

With the power of the RP2040 microcontroller and full compatibility with your favorite Arduino Uno shields, the RP-Duino is the perfect blend of performance and flexibility. Its 5V-tolerant GPIO means seamless integration with existing 5V hardware—no more worrying about level shifters or compatibility issues.
Whether you're a hobbyist, engineer, or educator, the RP-Duino offers unmatched versatility for creating powerful, innovative solutions.
Don't settle for limitations — upgrade to the RP-Duino today and bring your ideas to life!
MitchElectronics Stripboards - Now Available
Reimagine your electronics prototyping with ME Stripboards – engineered for modern makers and built to last. Say goodbye to outdated materials and fragile designs, and experience the strength, versatility, and innovation of our range. Perfect for both through-hole and surface-mount components, ME Stripboards are designed to meet the demands of today’s projects. Shop Now and Upgrade Your Builds!
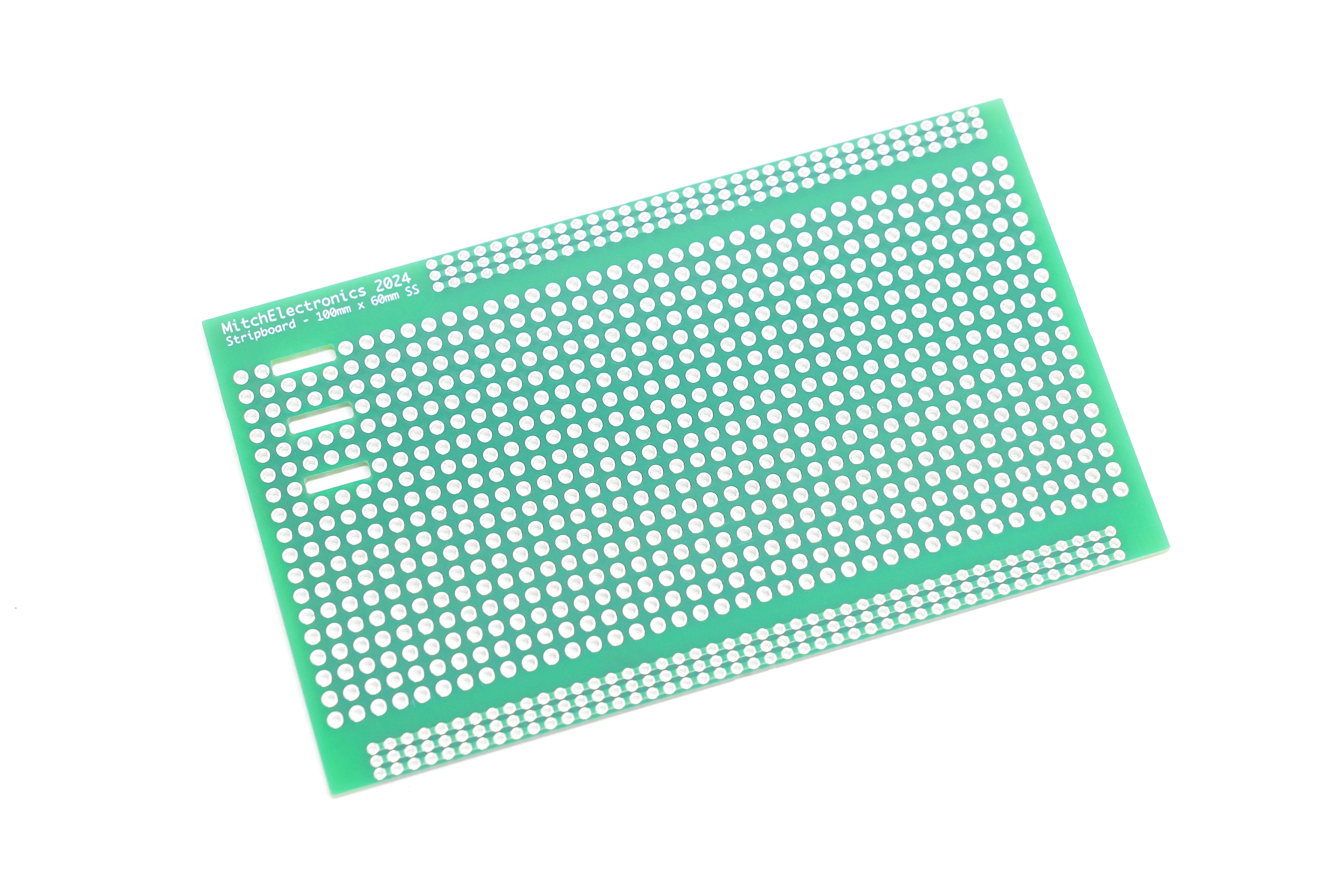
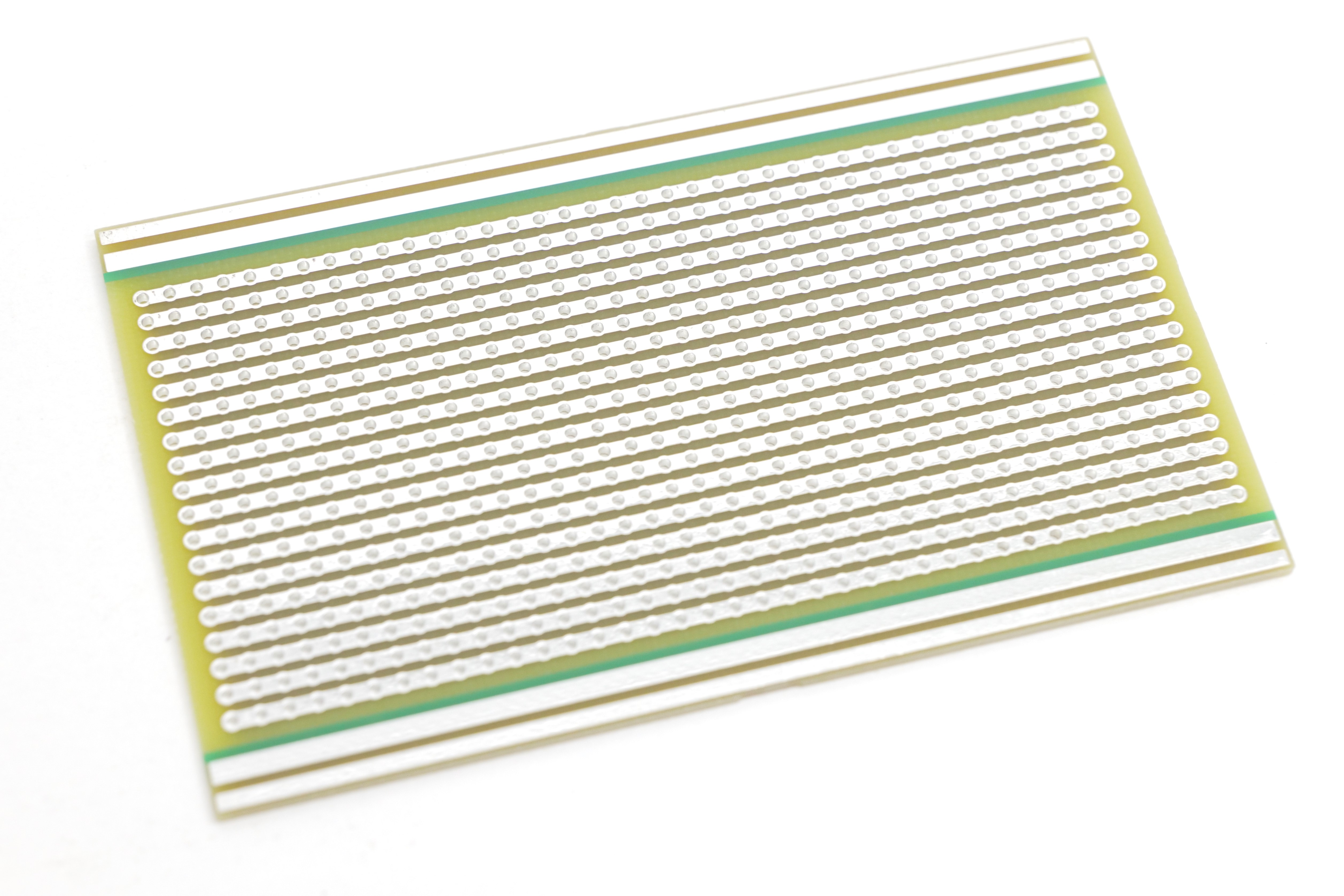
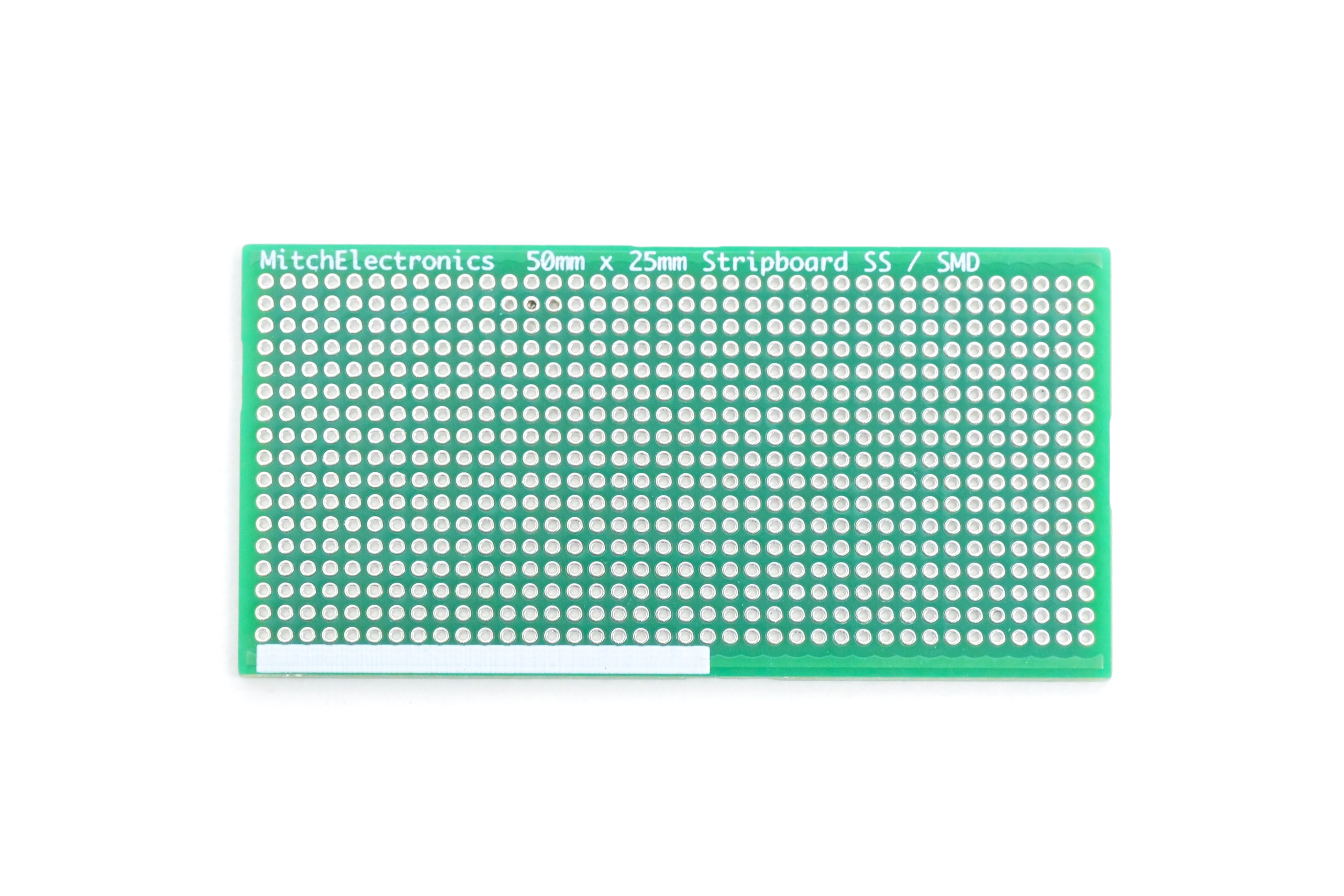
Reimagine your electronics prototyping with ME Stripboards – engineered for modern makers and built to last. Say goodbye to outdated materials and fragile designs, and experience the strength, versatility, and innovation of our range. Perfect for both through-hole and surface-mount components, ME Stripboards are designed to meet the demands of today’s projects. Shop Now and Upgrade Your Builds!



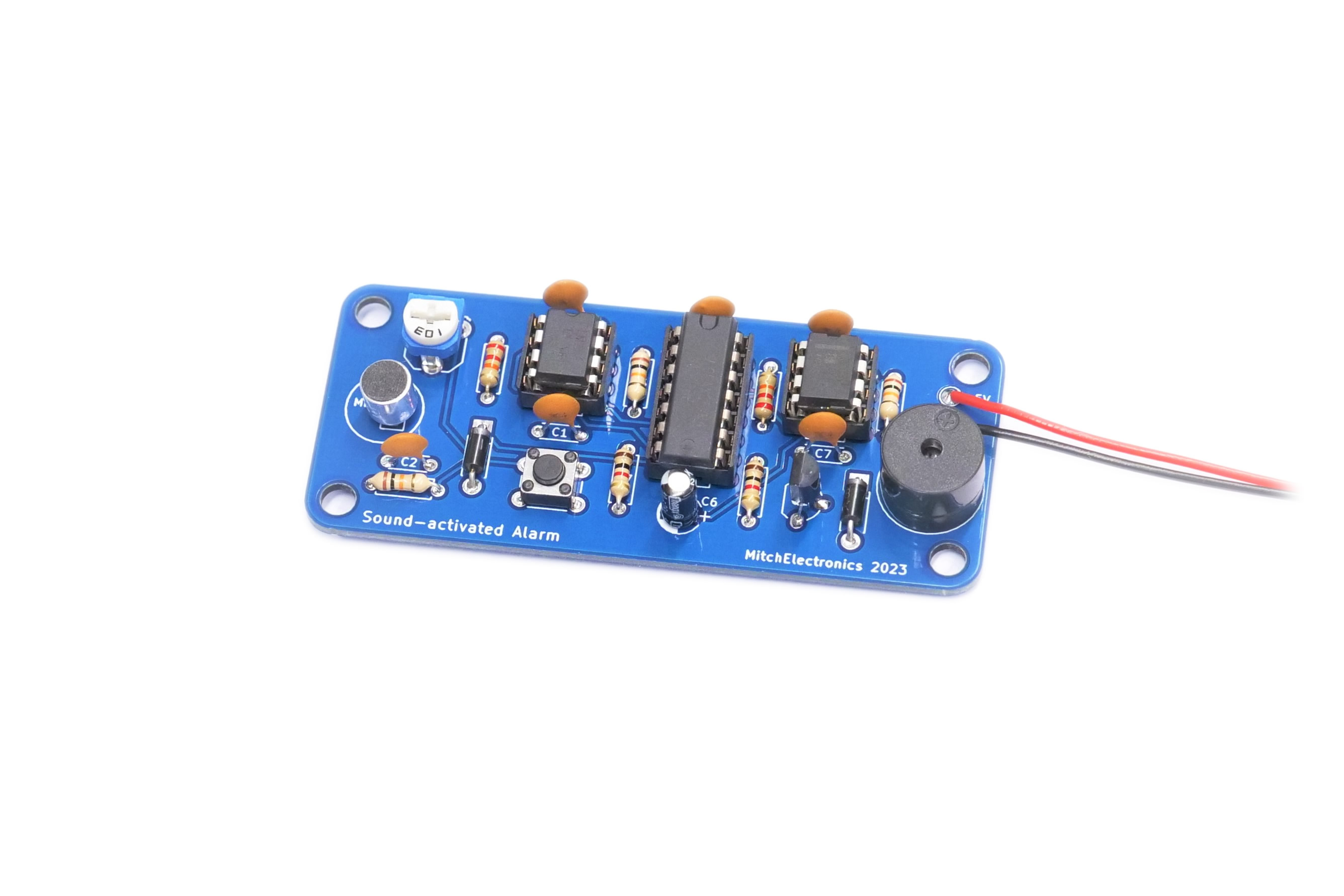
Latest DIY Electronic Kits
About Us
MitchElectronics is an electronics kit designer and manufacturer based in Stratford-Upon-Avon, the heart of the UK. Our electronic kits are specifically targeted at all levels of education, whether it is someone who has started a new journey into the realm of electronics, or someone who is looking to brush up their soldering skills.
Founded by Robin Mitchell in 2011, MitchElectronics has years of experience in designing electronic kits and resources that accompany them. The founding principle of MitchElectronics, which still holds true today, is to provide high qualtiy electronic kits to educators, makers, and engineers at affordable prices. We believe that because the electronics industry develops cheaper parts each year, these savings should be passed onto consumers. Furthermore, we also believe that electronic kits should come with numerous amounts of resources that not only provide clear instructions on how to build them, but also educate the user on how and why the kit works. As such, we have made it our mission to make the best instructions on the market.
In addition to our manufacturing capabilities, we also offer a range of services designed to support our customers throughout the entire product development cycle. From initial concept to final product, our team of experienced engineers is available to provide guidance and support every step of the way. We understand that product development can be a complex and challenging process, which is why we offer a range of services designed to help our customers bring their ideas to life. Whether it's designing a new product from scratch or refining an existing design, our team of experts is available to provide the guidance and support needed to bring any project to fruition.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you turn your ideas into reality.