

If you find yourself inside on a rainy day and without dice to play your favourite board games then look no further as the MitchElectronics Electronic Dice kit is just for you!
Built using three main sub-circuits this kit will simulate a dice with a simple cool-down system so you can watch the numbers roll. Press and hold the switch to start the dice rolling and then let go when your feeling lucking for that number which gets you past those expensive hotels or away from that ladder!
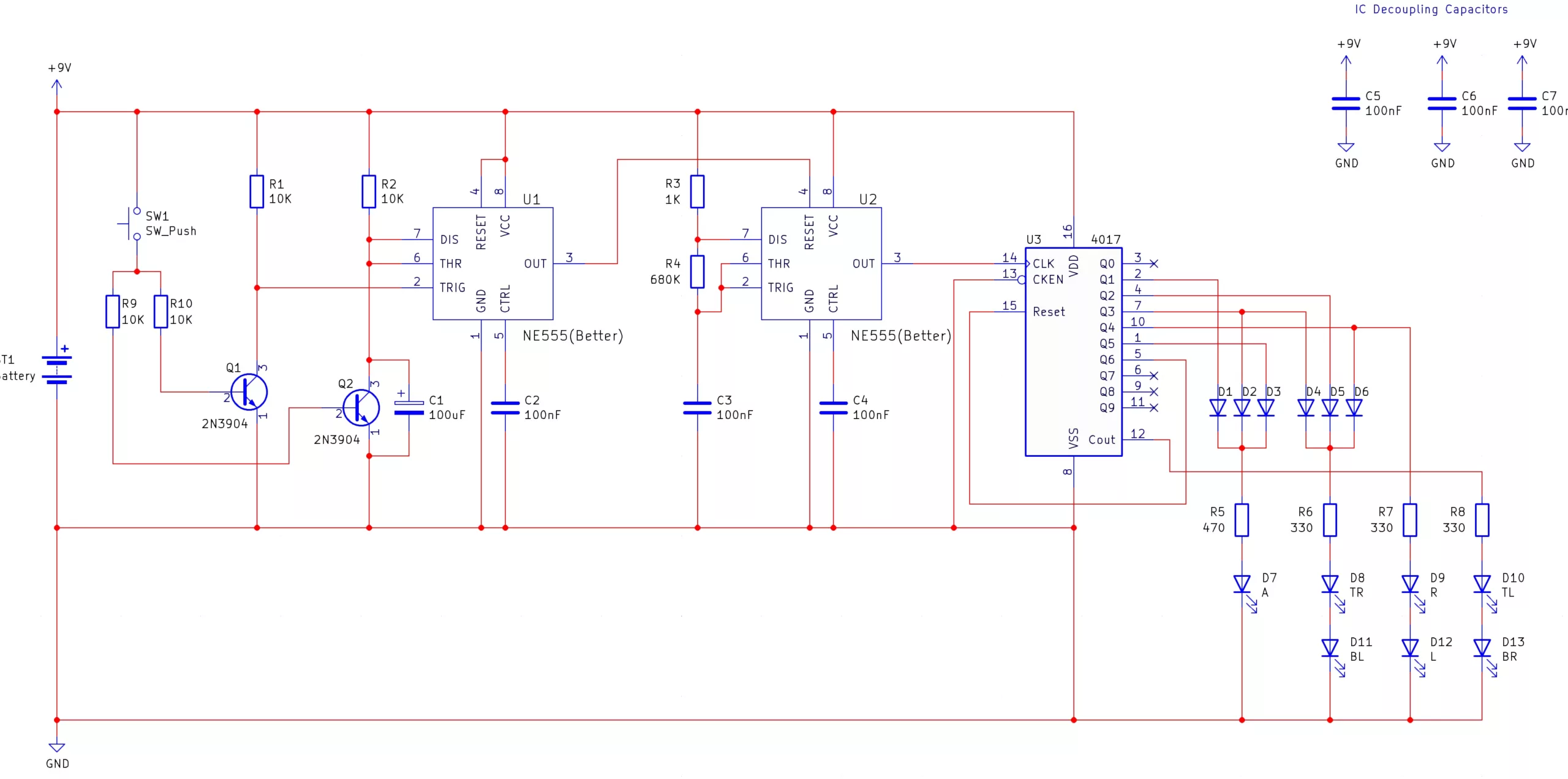
The Electronic Dice kit is an … electronic dice … which can be used in place of dice for board games and other dice applications. When the user presses and holds the switch (SW1), the circuit rolls the dice and when the user lets go of the roll button the dice continue to roll for a short amount of time before landing on the final value.
This project relies on three main sub-circuits which include
✓ - 555 Monostable circuit (U1)
✓ - 555 Astable circuit (U2)
✓ - 4017 counter (U3)
The function of the monostable and astable will not be covered here but can be learned from the other MitchElectronics kits found in the links above.
When the button is pressed and held the two transistors Q1 and Q2 are turned on. Q1 is connected to the trigger input of the 555 monostable U1 and so this causes the monostable to trigger. However, Q2 is connected across the timing capacitor C1 for the monostable and this discharges C1. C1 can only begin to charge when the user releases the button and so this is a 555 monostable that can be retriggered as well as held before starting the countdown.
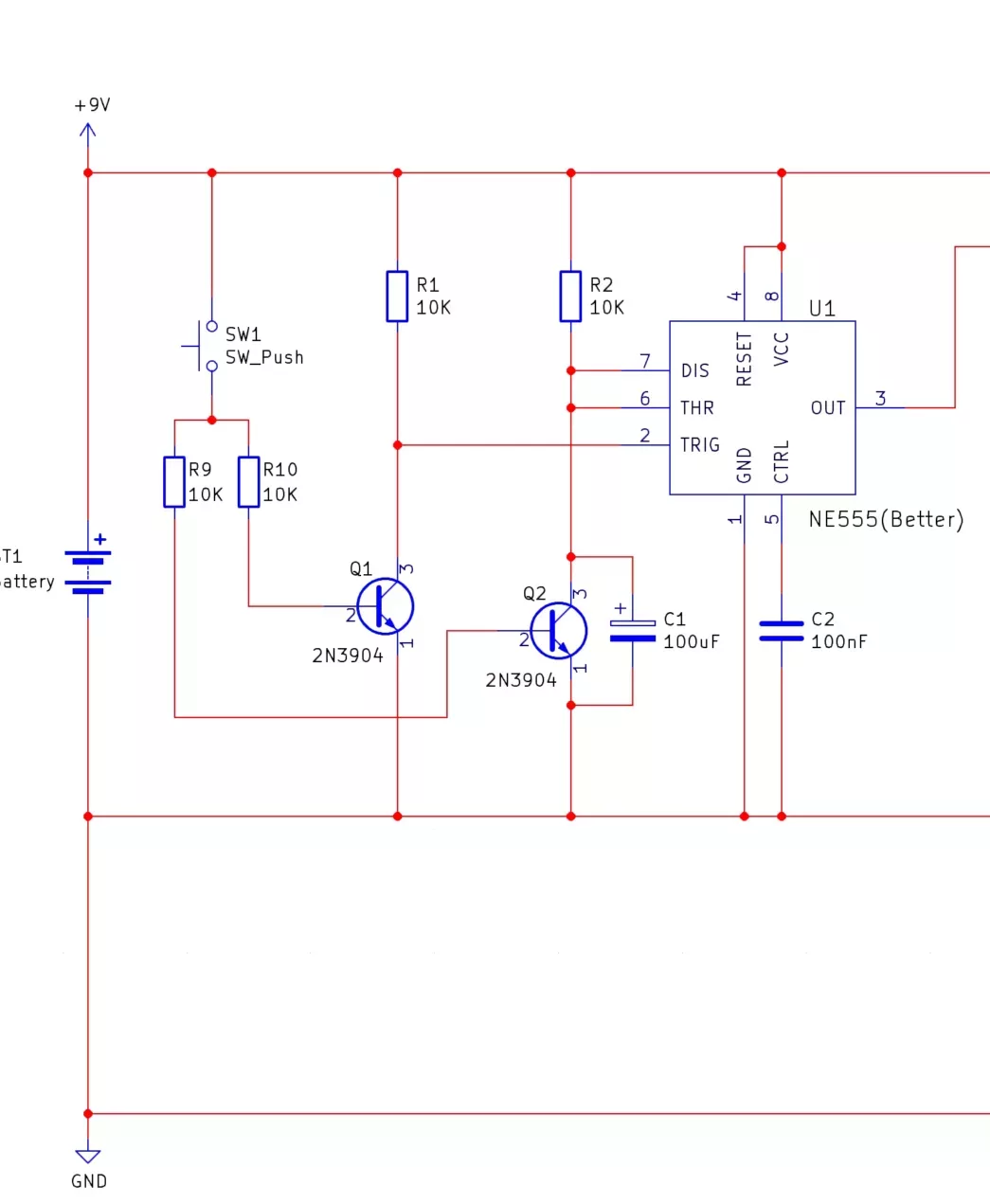
The 555 monostable (U1) is used to enable the 555 astable (U2) which acts as the clock source for the dice. Normally, the 555 monostable output is low and this keeps the 555 astable from oscillating but when the button is pressed and the monostable output goes high the 555 astable (U2) begins to oscillate.
The 555 astable is connected to the 4017 counters clock input so every time the 555 astable output (U2) goes from low to high the 4017 increments. The outputs of the 4017 are configured with diodes to create the pattern of the dice faces in the LEDs and upon counting more than 6 times the 4017 resets itself (by connecting Q6 which is the 7th output to the reset input).
| Component | PCB Reference | Quantity | Looks Like |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 DIP Socket | U1, U2 | 2 |  |
| 16 DIP Socket | U3 | 1 |  |
| 555 Timer IC | U1, U2 | 2 |  |
| 4017 Counter IC | U3 | 1 |  |
| 2N3904 NPN Transistor | Q1, Q2 | 2 |  |
| 330R Resistor | R6, R7, R8 | 3 |  |
| 470R Resistor | R5 | 1 | 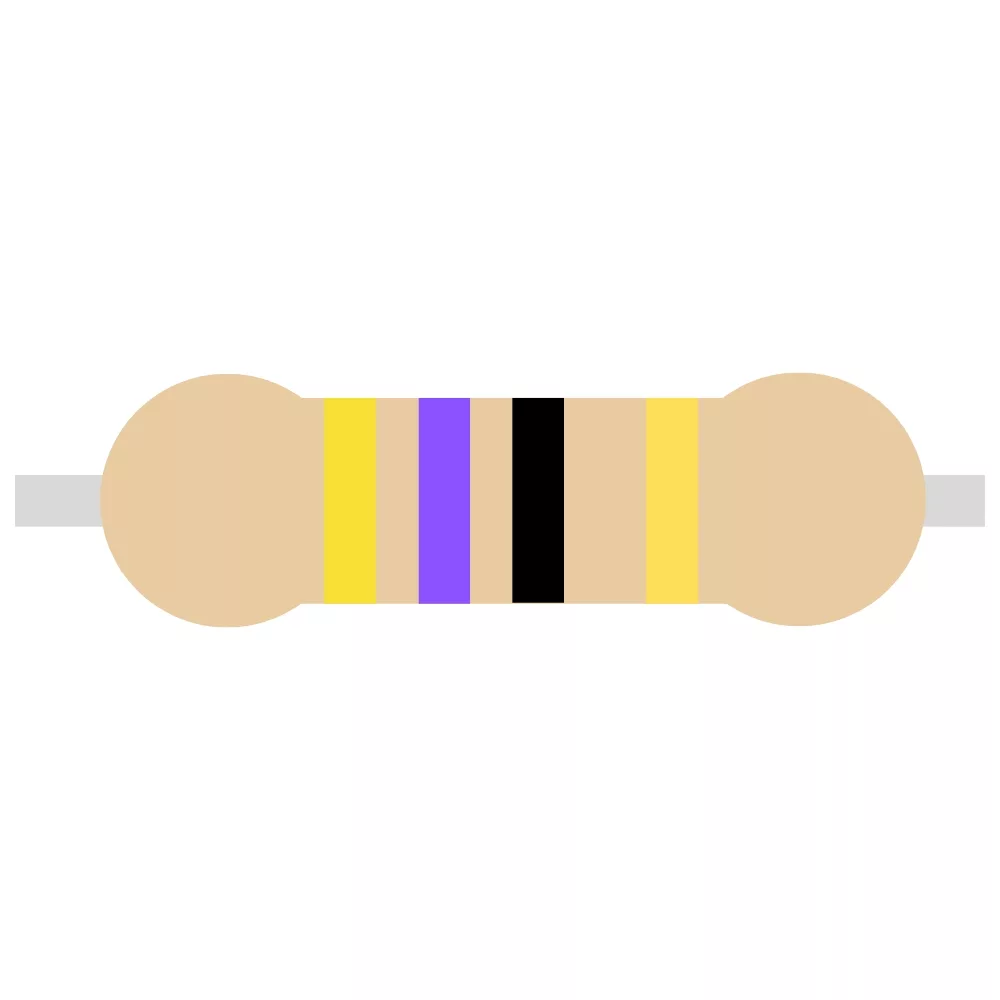 |
| 1K Resistor | R3 | 1 | 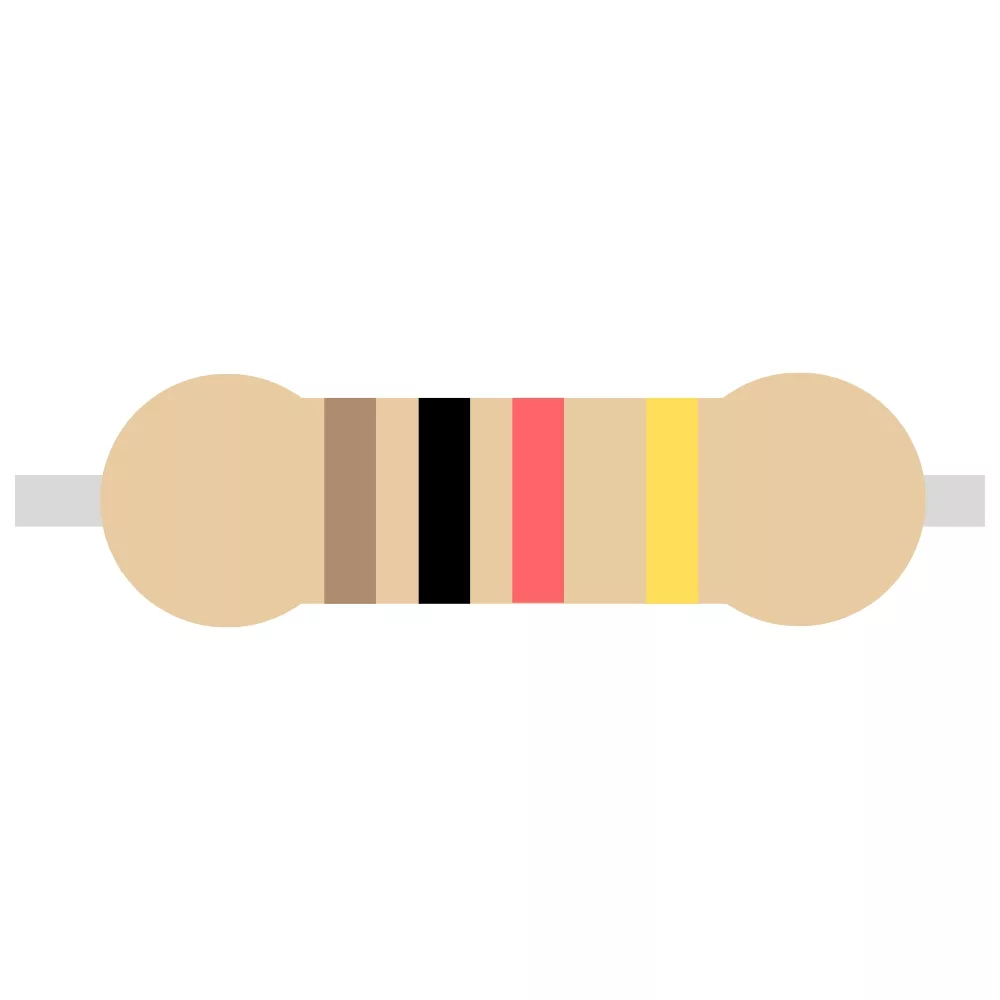 |
| 10K Resistor | R1, R2, R9, R10 | 4 | 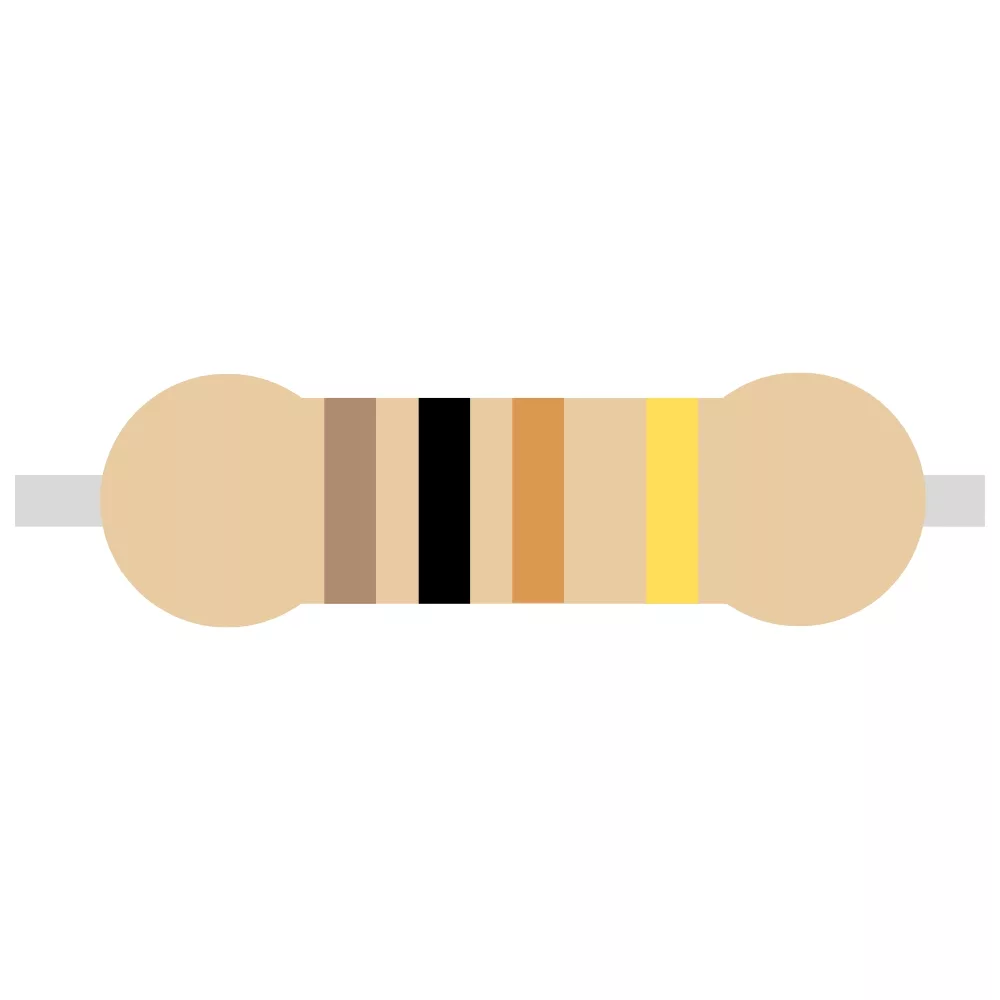 |
| 680K Resistor | R4 | 1 | 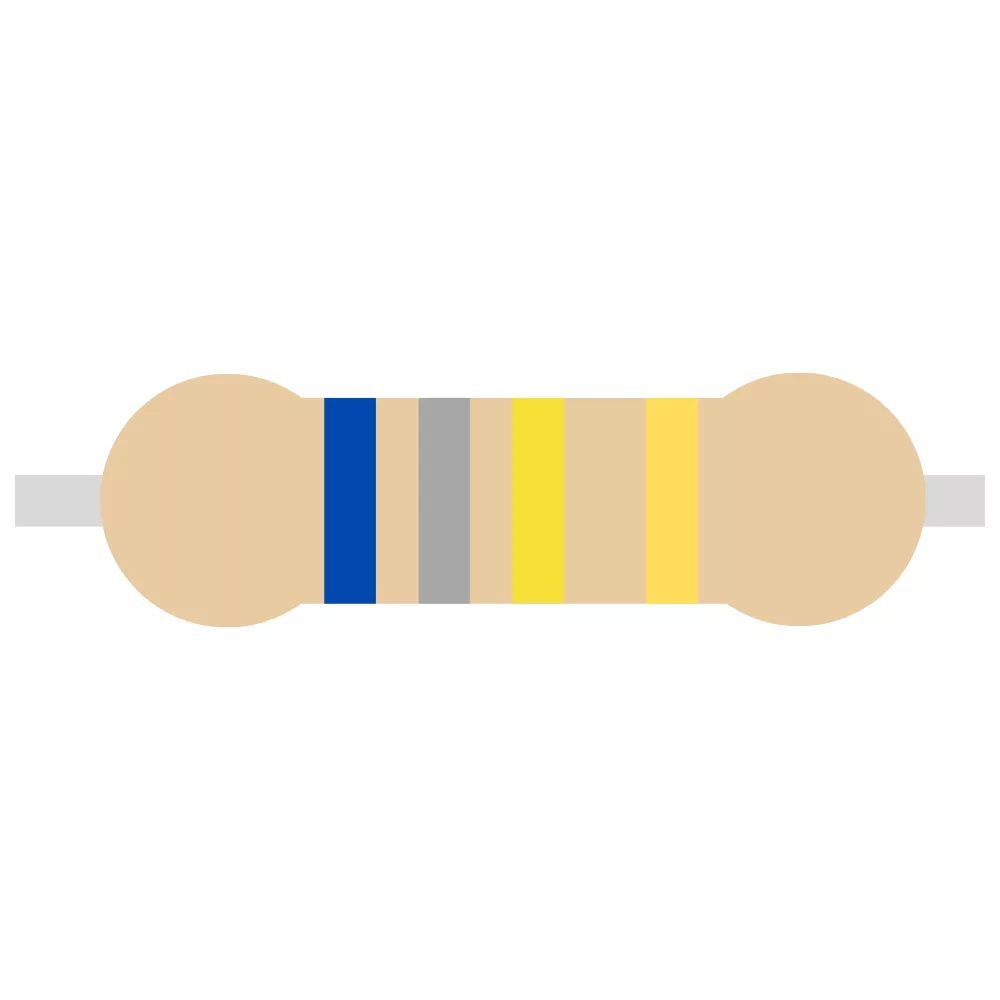 |
| 100nF Ceramic Disc Capacitor | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7 | 6 |  |
| 100uF Electrolytic Capacitor | C1 | 1 |  |
| Tactile Switch | SW1 | 1 |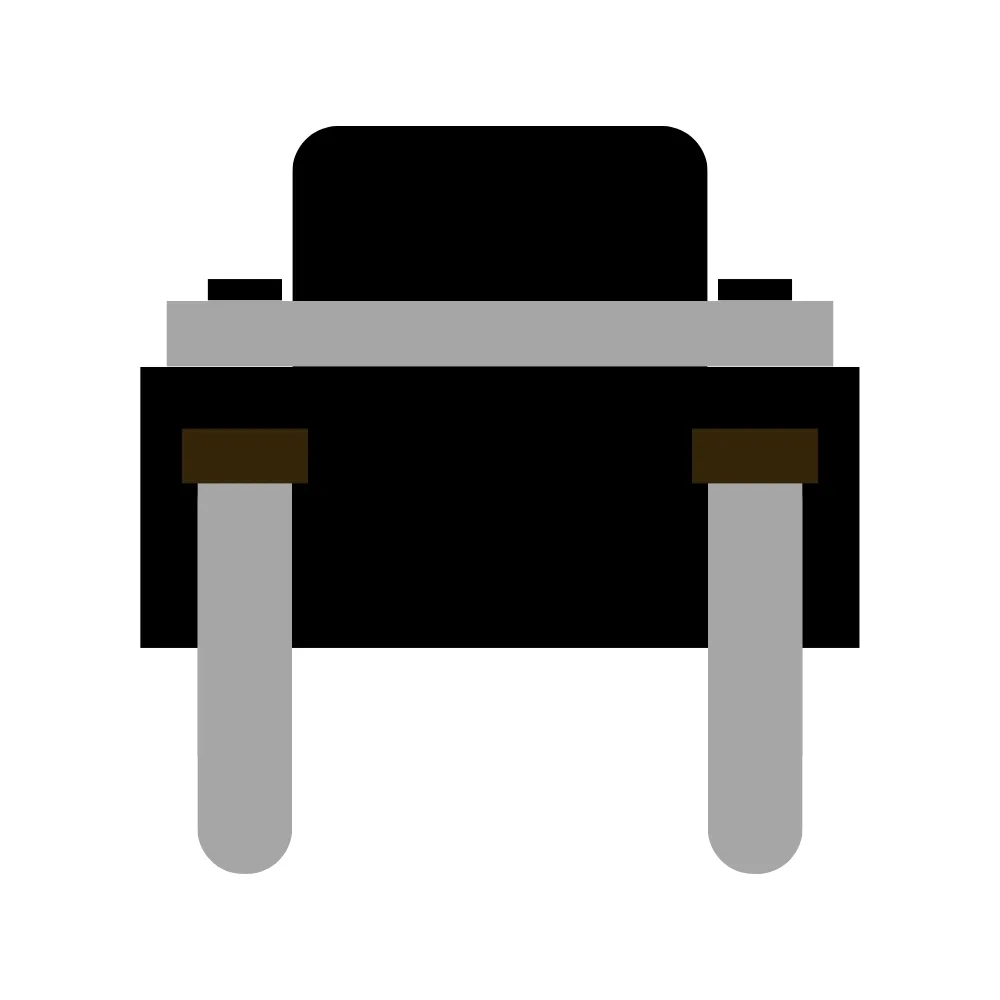  |
| 3mm Red LED | D7 - D13 | 7 |  |
| 1N4148 Diode | D1 - D6 | 6 |  |
| PP3 Connector | BT1 | 1 |  |

By far, the best use for the Electronic Dice Kit is board games. The project could easily be mounted inside an enclosure while the LEDs are made visible through an opening with semi-transparent black acrylic.
But this project could easily be combined with multiple Electronic Dice Projects to create two simultaneous dice that roll either in sync or roll one after the other. Either way, it would be impossible to cheat with these dice!

To learn more about how to solder electronic components, download the Electronics Construction Manual free using the button below
Electronics Construction Manual
When soldering components, it is essential that you do so in a particular order, so that it is easy to add components and get to their legs. Generally, you always start with the smaller components (such as resistors and capacitors), before moving onto the larget parts (potentiometers and ICs).
Soldering Guide
Modify the dice to slowly count down instead of suddenly. This could be done by combining the Voltage Controlled Oscillator kit with an RC circuit
As the voltage across an RC tank circuit falls, the output frequency of the VCO falls, and this would result in a slower count
Eventually, a comparator would reset the VCO and prevent further counts after the RC voltage has reached a minimum level